Open Folder in Visual Studio Code and write a C++ program
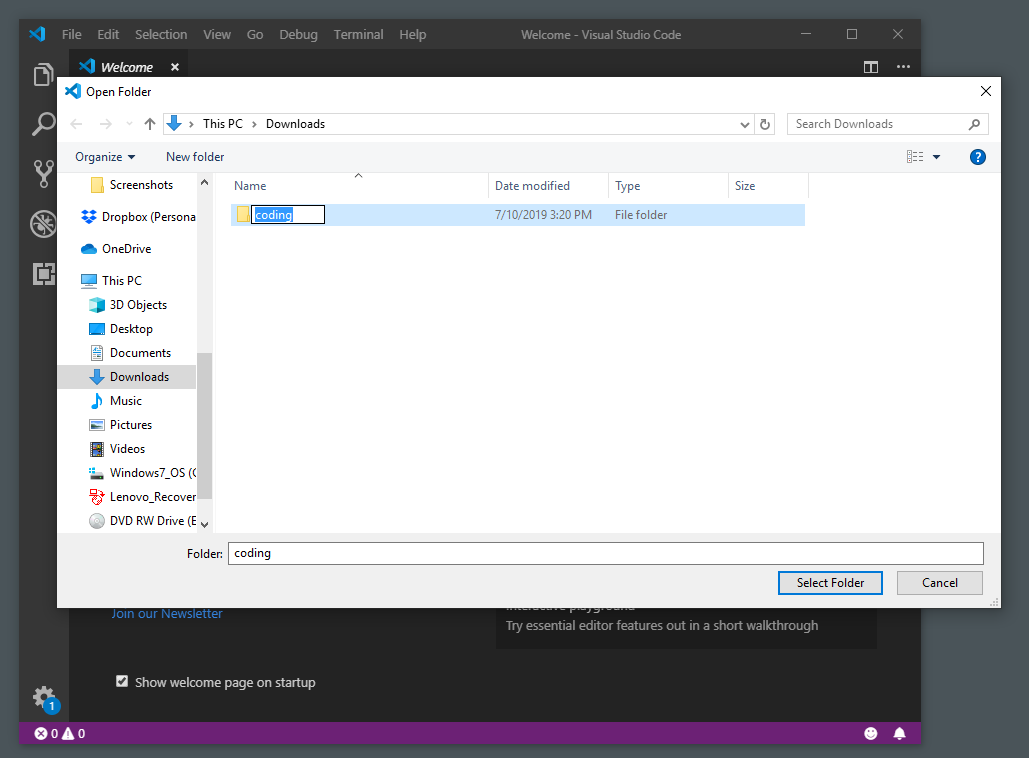
- Close Visual Studio Code if it’s currently open. Then Launch Visual Studio Code. Choose File -> Open Folder…
- Create a brand new folder at any location of your choosing. In this example, the new folder will be called coding.
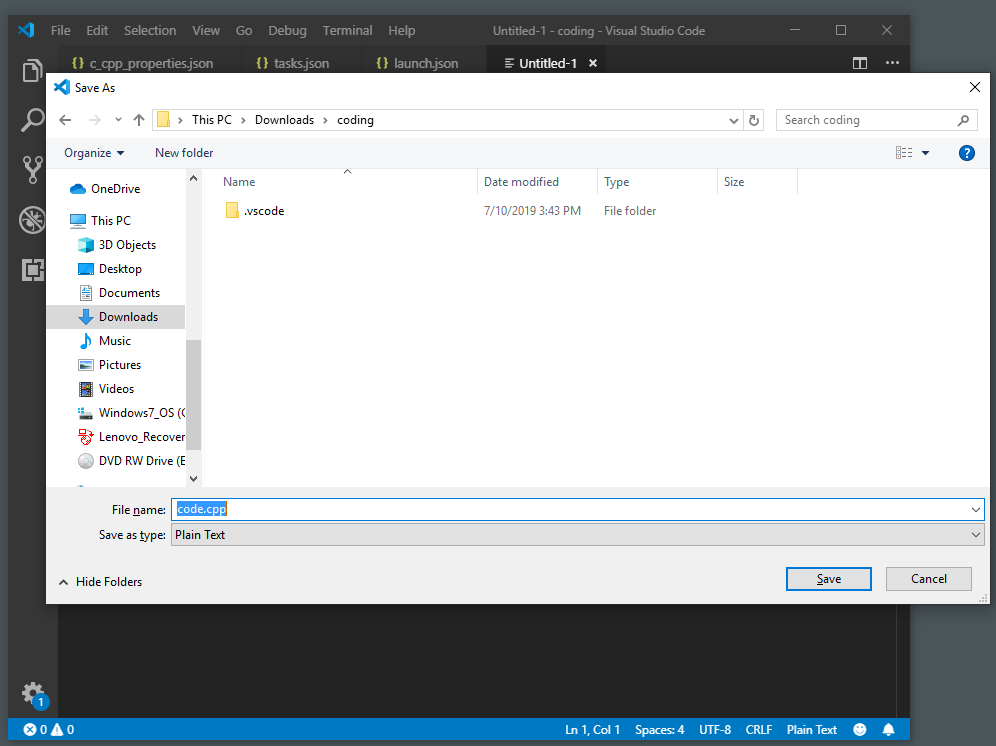
- In the main VS Code editor, click on File -> New File, and then press Ctrl+S to save it as “code.cpp”.
- Install C++ extension for VS Code.
Set compilerPath
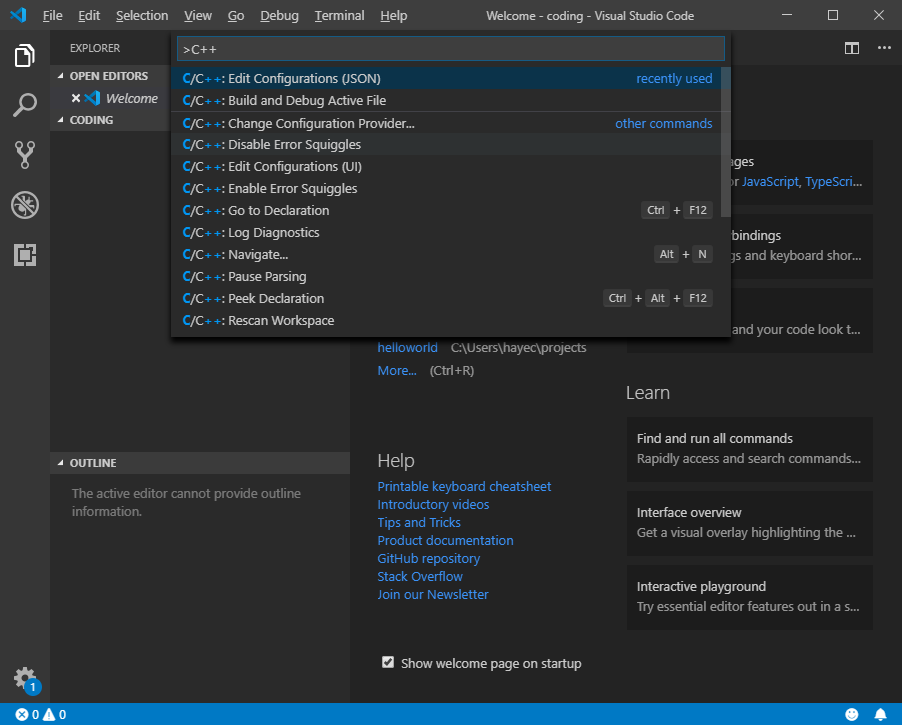
- Press Ctrl+Shift+P, start typing “C/C++” and then choose Edit Configurations (JSON) from the list of suggestions. VS Code creates a file called c_cpp_properties.json and populates it with default settings.
- Find the
compilerPath setting and paste in the full path name of g++.exe in the Mingw-w64 bin folder you have just appended to the Path variable. (C:\\Mingw-w64\\mingw32\\bin\\g++.exe, notice how you have to do double “\” due to json convention)
- Set
intelliSenseMode to gcc-x64.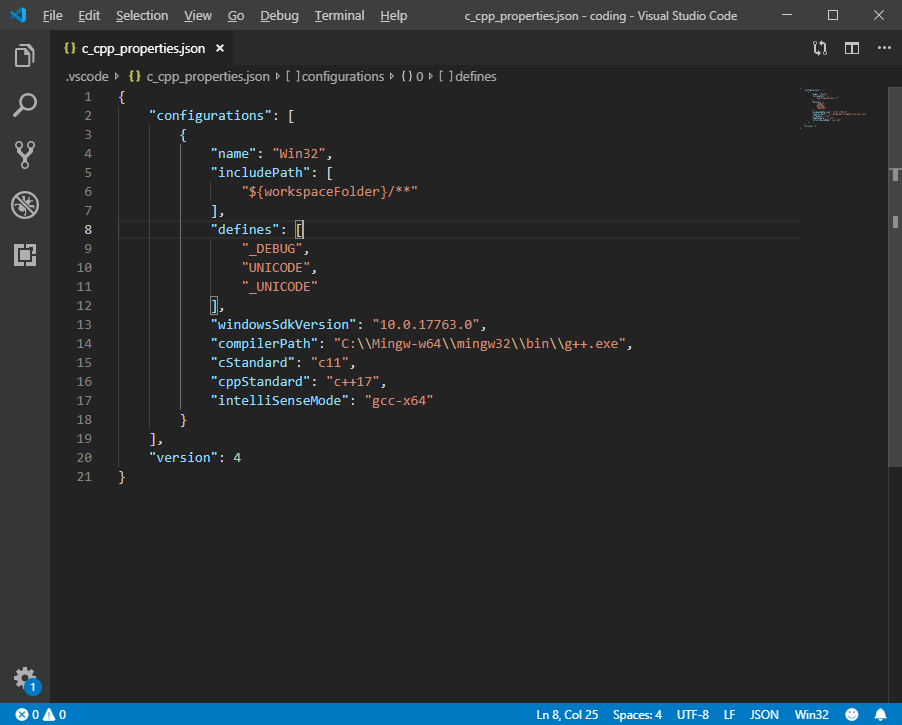
- Your
c_cpp_properties.json file should look like this:
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Win32",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**"
],
"defines": [
"_DEBUG",
"UNICODE",
"_UNICODE"
],
"windowsSdkVersion": "10.0.17763.0",
"compilerPath": "C:\\Mingw-w64\\mingw32\\bin\\g++.exe",
"cStandard": "c11",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "gcc-x64"
}
],
"version": 4
}
Create a build task
- Next, Press Ctrl+Shift+P again and start typing “task” and choose Tasks: Configure Default Build Task from the list of suggestions, then choose Create tasks.json file from template. Then choose MSBuild. VS Code creates a default tasks.json file in the editor.
- Find the
command setting and change it to g++.
- Change
args setting to [ "-g", "-o", "a.exe", "code.cpp"]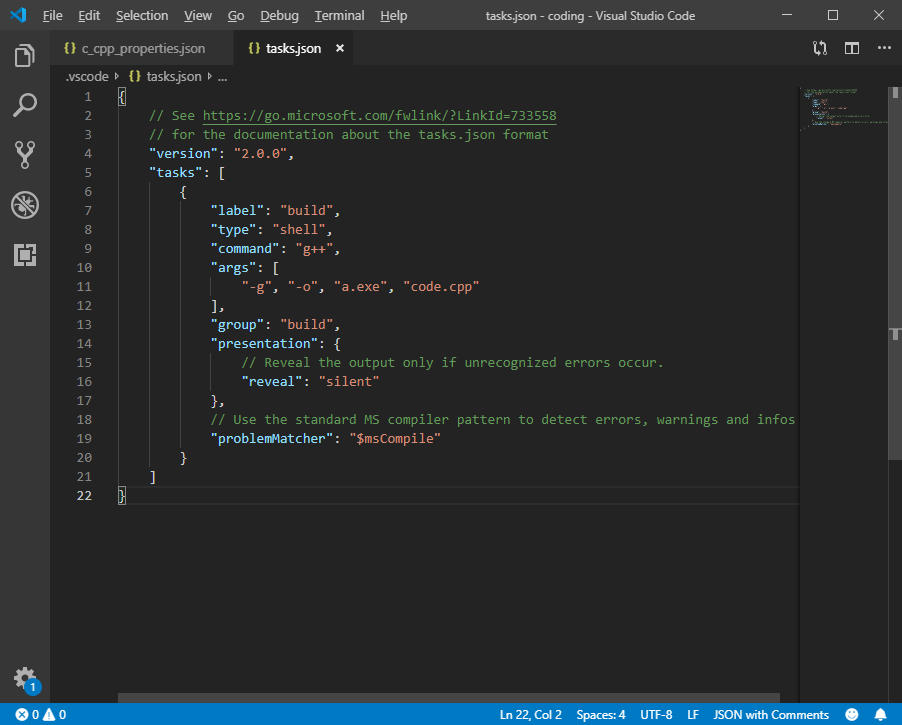
- Your
tasks.json should look like this:
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "build",
"type": "shell",
"command": "g++",
"args": ["-g", "-o", "a.exe", "code.cpp"],
"group": "build",
"presentation": {
"reveal": "silent"
},
"problemMatcher": "$msCompile"
}
]
}
Configure debug settings
Next, we’ll configure VS Code so that it launches the gdb debugger properly.
- Click Debug -> Open Configurations, and then choose C++ (GDB/LLDB) from the list of suggestions. VS Code creates a default launch.json file in the editor.
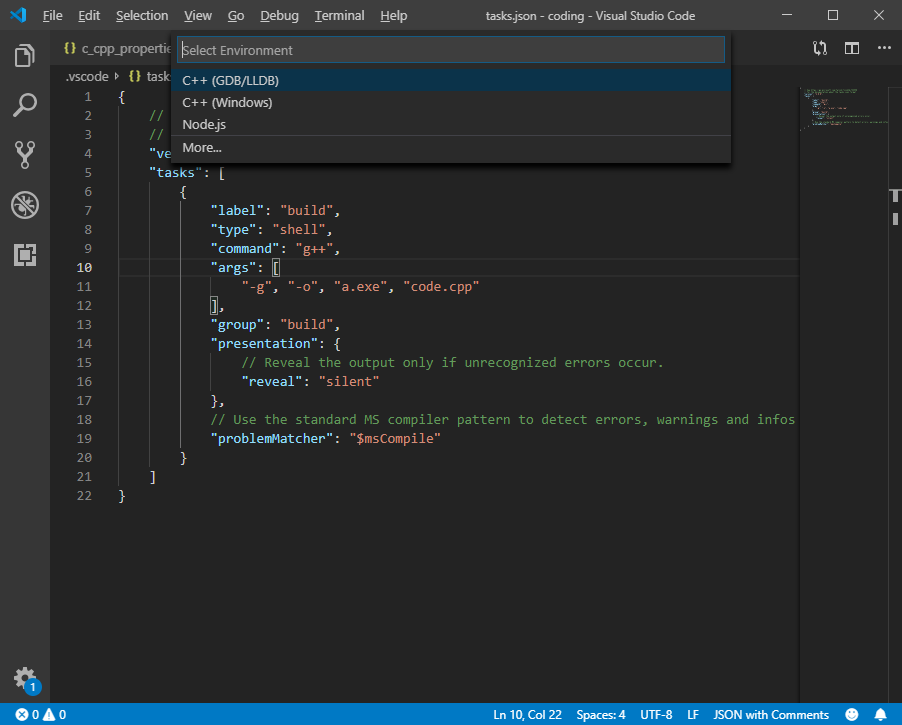
- Find the
program setting and delete everything except for the last part ${workspaceFolder}/a.exe.
- Find the
miDebuggerPath and point it to the gdb file in your Mingw-w64 bin folder, i.e. C:\\Mingw-w64\\mingw32\\bin\gdb.exe
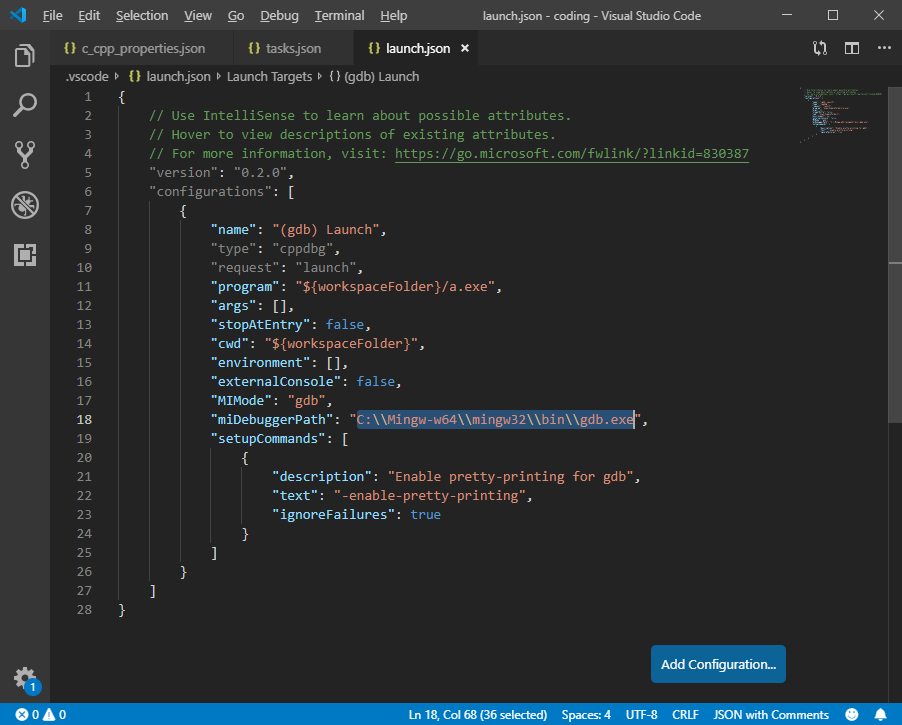
- Your complete
launch.json file should look like this:
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/a.exe",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"miDebuggerPath": "C:\\Mingw-w64\\mingw32\\bin\\gdb.exe",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
}
]
}
Set breakpoint and debug
- Go to code.cpp in the editor, write your C++ program and Press Ctrl+Shift+B and then Enter to compile.
- Then set a break point and Press F5 to debug.
Additional bonus settings
- After any changes to source code, always remember to Ctrl+Shift+B to build before you run debug. If you want F5 to always rebuild the code by default, insert this right below the line of
program setting in the launch.json file.
"preLaunchTask": "build",
- Ideally you want the debug output to be on a separate console. In
launch.json, find externalConsole setting and change it to true.







